.gif)
NASA today launched the world's full-scale mission to test its technology to defend the Earth against potential asteroids or comet hazards.
 |
| Rendered image from NASA |
To slightly change the asteroid's motion and protect Earth from an asteroid that might pose an impact hazard
Dubbed as the Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART), the technology was launched Wednesday at 1:21 AM EST on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California.
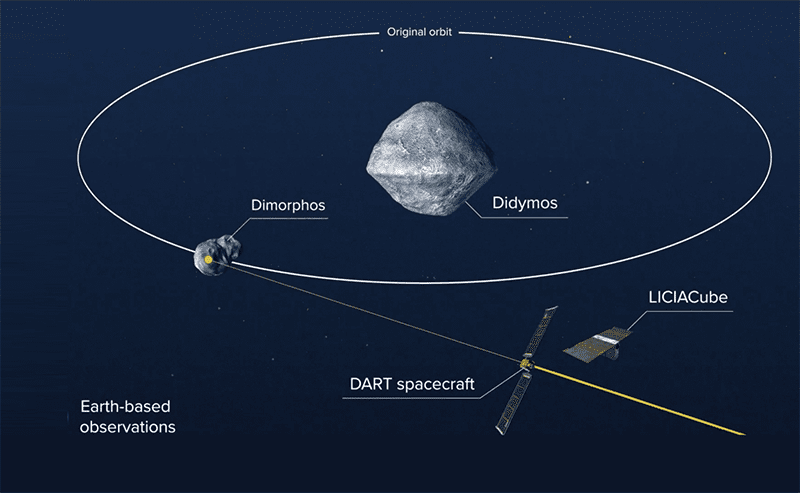 |
| DART's mission |
In a press statement, NASA said built and managed by the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. It is one part of NASA's larger planetary defense strategy and will hit a known asteroid that is not a threat to Earth.
The goal of the mission is to slightly change the asteroid's motion in a way that can be accurately measured using ground-based telescopes.
NASA notes that DART will show that a spacecraft can autonomously navigate to a target asteroid and intentionally collide with it. It is a deflection method called kinetic impact.
The test is said to provide important data to help better prepare for an asteroid that might pose an impact hazard to planet Earth, should one ever be discovered, NASA stressed.
The space agency also shared that LICIACube, a CubeSat riding with DART and provided by the Italian Space Agency (ASI), will be released prior to DART's impact to capture images of the impact and the resulting cloud of ejected matter.
Then after roughly four years after DART's impact, ESA's (European Space Agency) Hera project will conduct detailed surveys of both asteroids, with particular focus on the crater left by DART's collision and a precise determination of Dimorphos' mass.
DART will basically have a one-way trip to Didymos asteroid system with a pair of asteroids. The target is the moonlet Dimorphos. Dimorphos is 530 feet (160 meters) in diameter. Didymos is 2,560 feet (780 meters) in diameter.
Dimorphos orbits Didymos at much a slower relative speed than the pair orbits the Sun, so DART's kinetic impact within the binary system can be measured much more easily than a change in the orbit of a single asteroid around the Sun.

.gif)




















Post a Comment